On-Demand Webinars
MTBE and TBA: Part 1:
Update and Review of These Two Gasoline Additive Co-Contaminants
 Although no longer used in the United States, methyl tertiary butyl ether (MTBE) remains an important groundwater contaminant at many gasoline-impacted sites. MTBE is the most prominent example of a group of alkyl ethers used worldwide as oxygenates and octane enhancers for unleaded gasoline. Its primary biodegradation product, tertiary butyl alcohol (TBA), is also detected in groundwater at sites impacted by MTBE-containing gasoline. Both of these compounds are highly water soluble and mobile and can be problematic compounds to characterize and remediate in groundwater. Although no longer used in the United States, methyl tertiary butyl ether (MTBE) remains an important groundwater contaminant at many gasoline-impacted sites. MTBE is the most prominent example of a group of alkyl ethers used worldwide as oxygenates and octane enhancers for unleaded gasoline. Its primary biodegradation product, tertiary butyl alcohol (TBA), is also detected in groundwater at sites impacted by MTBE-containing gasoline. Both of these compounds are highly water soluble and mobile and can be problematic compounds to characterize and remediate in groundwater.
This two-part webinar series provides a comprehensive overview of MTBE and TBA as groundwater contaminants. Part 1 of this webinar series discusses the chemical and physical properties of these two compounds, their environmental fates and impacts, and the main biodegradation processes that attenuate these compounds. This webinar also provides an up-to-date summary of the advanced chemical and biomolecular methodologies available to detect and quantify biodegradation of these important and difficult to remediate compounds.
Highlights of Part 1:
- History of MTBE and TBA as gasoline components
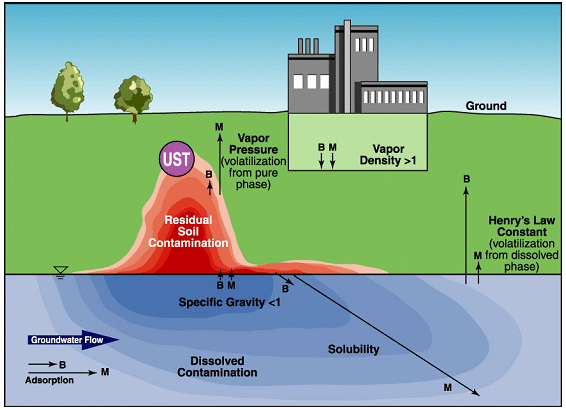
- Physical and chemical properties of MTBE and TBA
- Transport of MTBE and TBA in groundwater
- Biodegradation mechanisms for MTBE and TBA
- Detection methodologies for oxygenates, TBA, and oxygenate-degrading microorganisms
Webinar participants will gain an understanding of:
- Physical and chemical properties of MTBE and TBA that differentiate them from other major gasoline components
- Potential sources of MTBE and TBA and subsequent environmental distribution of these chemicals
- How biodegradation processes impact these compounds, the environmental conditions that can control these biological processes and the different types of microorganisms responsible for MTBE and TBA biodegradation
- How these chemicals can be detected and quantified and how modern chemical and molecular diagnostic tools can be used to identify the sources and fates of these compounds in groundwater systems
Instructors Bio
 Dr. Mike Hyman is an environmental microbiologist with 30 years experience in the characterization of microbial degradation processes directed at important environmental contaminants including chlorinated solvents, MTBE, and other gasoline components. Dr. Hyman's current research is focused on non MTBE-related sources if TBA, the biodegradation of 1,4-dioxane by hydrocarbon-oxidizing microorganisms and environmental proteomics. Dr. Hyman has been a member of the ITRC "MTBE and other Fuel Oxygenates" and is currently a member of the "Environmental Molecular Diagnostics" and "Petroleum Vapor Intrusion" teams. Dr. Hyman received his BS from University College London and his PhD from the University of Bristol. Dr. Hyman is currently a Professor of Microbiology at North Carolina State University. Dr. Mike Hyman is an environmental microbiologist with 30 years experience in the characterization of microbial degradation processes directed at important environmental contaminants including chlorinated solvents, MTBE, and other gasoline components. Dr. Hyman's current research is focused on non MTBE-related sources if TBA, the biodegradation of 1,4-dioxane by hydrocarbon-oxidizing microorganisms and environmental proteomics. Dr. Hyman has been a member of the ITRC "MTBE and other Fuel Oxygenates" and is currently a member of the "Environmental Molecular Diagnostics" and "Petroleum Vapor Intrusion" teams. Dr. Hyman received his BS from University College London and his PhD from the University of Bristol. Dr. Hyman is currently a Professor of Microbiology at North Carolina State University.
| Fee: |
299.00 USD Per Webinar
|
| Materials and Downloads: |
Session Slides (PDF)
Record of Attendance Form (PDF)
|
Number of
Participants: |
AS OF JUNE 1, 2020, WEBINARS ARE PRICED FOR INDIVIDUALS WORKING ALONE. Pricing is discounted for individual registrations for people working alone.
|
Continuing
Education
Certificates: |
$14.95 each. Official CEU certificates are available as an option. After successful completion of this webinar, a link will be provided to order a certificate.
|
| Access: |
On-demand, anytime 24/7. |
| Discounts: |
Buy 3 on-demand webinars, and get 3 on-demand webinars for free!
|
| Duration: |
90 minutes |
| PDH Earned: |
1.5 hours |
| |
|
| Instructor(s): |
Michael Hyman, PhD |
|
Become A Member
It's Free, It's Easy and as a
Member you'll enjoy...
- Exclusive Videos
- Special Pricing
- And Much More
|
|
Join
|
Learn More
|
Association of Environmental
& Engineering Geologists
|