On-Demand Webinars
ENVIRONMENTAL ISOTOPES FOR CONTAMINANT SOURCE IDENTIFICATION:
Advances in Tools, Technologies and Applications
Isotopes As A Key To Determining Contaminant Sources
 Knowing the contaminant source is a fundamental requirement for remediation, and isotope investigations can be particularly helpful in determining the contaminant source in groundwater, surface water, and soil gas. This webinar presents case studies where isotopes were used to demonstrate: Knowing the contaminant source is a fundamental requirement for remediation, and isotope investigations can be particularly helpful in determining the contaminant source in groundwater, surface water, and soil gas. This webinar presents case studies where isotopes were used to demonstrate:
- Common isotopes used in environmental investigations:
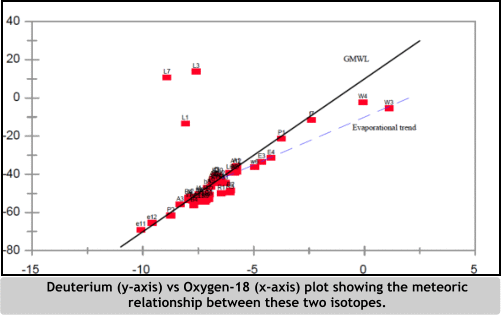
- Deuterium
- Oxygen-18
- Carbon-13
- Carbon-14
- Tritium
- Strontium
- Ntirogen-15 isotope of ammonia
- Natural and anthropogenic concentrations of these isotopes in the environment
- How isotope data is analyzed with respect to other geochemical data through:
- Time-series analysis
- Geochemical fingerprinting
- Isotope evaluation
The webinar will address:
- When isotope evaluation is appropriate
- Planning an isotope sampling and analytical event: the field sampling and analytical methods you need to know
- How to interpret isotope results
- How results can determine the appropriate remediation response
In addition, this webinar will discuss how isotopes are used to understand the origin of:
- VOCs in groundwater contaminated by leachate from hazardous waste and municipal solid waste landfills
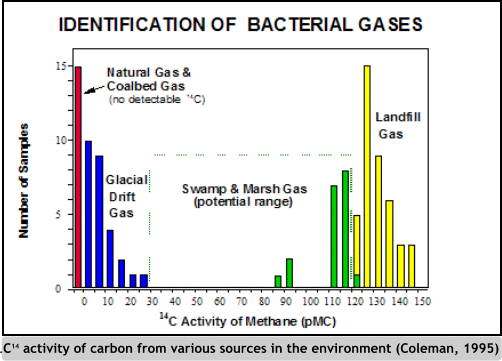
- Methane in soil gases and dissolved gases in groundwater leading to VOC detections
- Ammonia-nitrogen in groundwater
- Ammonia-nitrogen from salt water and marine muds
- Inorganic contaminants in groundwater
Instructors Bio
John Baker, MS-EE
 John Baker has over 40 years experience in implementing new technologies for more cost effective remediation and optimization of hazardous, nuclear and solid waste landfills. He previously worked 23 years for Waste Management, Inc. most recently as the Director of New Technology. In this role, Mr. Baker was responsible for developing innovative methods for environmental assessment including forensic contaminant sources for gas and liquids using geochemistry and environmental isotopes. John Baker has over 40 years experience in implementing new technologies for more cost effective remediation and optimization of hazardous, nuclear and solid waste landfills. He previously worked 23 years for Waste Management, Inc. most recently as the Director of New Technology. In this role, Mr. Baker was responsible for developing innovative methods for environmental assessment including forensic contaminant sources for gas and liquids using geochemistry and environmental isotopes.
Mr. Baker has also developed advanced remediation techniques and enhanced renewable energy production of active and closed landfills. Mr. Baker has evaluated over 200 innovative waste management technologies for energy production including pyrolysis, gasification, plasma arc, and other treatment/conversion methods. Technical feasibility and relative economics were included. Mr. Baker also was involved in early research starting in the late '70s with DOE and USEPA for potential of pyrolysis and gasification for waste to energy and remediation. He also assisted in permitting a plasma arc hazardous waste incinerator in the early '80s. Mr. Baker also provided consulting services for two gasification companies for citing and start-up demonstrations using MSW.
BS in Biology/Chemistry and MS in Environmental Engineering from University of Illinois, Urbana, IL 1971 & 1973
| Fee: |
299.00 USD Per Webinar
|
| Materials and Downloads: |
Session Slides (PDF)
Record of Attendance Form (PDF)
|
Number of
Participants: |
AS OF JUNE 1, 2020, WEBINARS ARE PRICED FOR INDIVIDUALS WORKING ALONE. Pricing is discounted for individual registrations for people working alone.
|
Continuing
Education
Certificates: |
$14.95 each. Official CEU certificates are available as an option. After successful completion of this webinar, a link will be provided to order a certificate.
|
| Access: |
On-demand, anytime 24/7. |
| Discounts: |
Buy 3 on-demand webinars, and get 3 on-demand webinars for free!
|
| Duration: |
90 minutes |
| PDH Earned: |
1.5 hours |
| |
|
| Instructor(s): |
John Baker, MS-EE |
|
Become A Member
It's Free, It's Easy and as a
Member you'll enjoy...
- Exclusive Videos
- Special Pricing
- And Much More
|
|
Join
|
Learn More
|
Association of Environmental
& Engineering Geologists
|